Feeding Livestock Naturally: Alternatives to Commercial Feed

Natural Feeding Options for Livestock

Livestock owners are increasingly turning to natural feeding options to enhance the health and well-being of their animals. By incorporating a variety of alternative feeds into their livestock’s diet, they not only provide a more diverse range of nutrients but also reduce dependency on conventional feed sources. From grasses and forages to legumes and root vegetables, there are numerous options available to cater to the nutritional needs of different types of livestock.
One key benefit of utilizing natural feeding options is the potential to improve the overall quality of meat, milk, or eggs produced by the animals. As livestock consume a more varied diet, they can develop stronger immune systems and exhibit better growth rates. Additionally, by incorporating a mix of grains, seeds, fruits, and vegetables, livestock can potentially experience a more balanced nutritional intake, leading to healthier and more resilient animals in the long run.
• Grasses and forages
• Legumes
• Root vegetables
Livestock owners can also benefit from cost savings by utilizing natural feeding options. By growing their own feed or sourcing locally produced alternatives, they can reduce expenses associated with purchasing commercial feed. This not only helps in managing production costs but also ensures a more sustainable approach to livestock farming.
In addition to the health benefits for the animals, natural feeding options can also have positive impacts on the environment. By reducing reliance on conventional feed sources that may be linked to deforestation or excessive use of pesticides, livestock owners can contribute to a more eco-friendly and sustainable agricultural system.
Furthermore, incorporating natural feeding options into livestock diets can help in promoting biodiversity on farms. Growing a variety of crops and plants for animal consumption not only provides different nutrients but also supports diverse ecosystems that are beneficial for overall farm health and resilience.
Overall, natural feeding options offer a holistic approach to livestock nutrition that promotes animal well-being, environmental sustainability, and cost-effectiveness for farmers. By exploring different alternatives and diversifying their animals’ diets, livestock owners can ensure healthier outcomes for both their animals and the planet.
Benefits of Using Alternative Feeds for Livestock

Alternative feeds offer various advantages for livestock owners. By incorporating a diverse range of feed sources into their animals’ diets, farmers can provide a more balanced and nutritious diet. This can lead to improved overall health and well-being of the livestock, resulting in better growth rates and reproductive performance. Additionally, alternative feeds can be a cost-effective option for livestock production, especially when traditional feed sources are expensive or scarce.
Furthermore, using alternative feeds can also have environmental benefits. By diversifying the feed sources, farmers can reduce their reliance on monoculture crops and minimize the environmental impact associated with intensive farming practices. This can contribute to sustainable livestock production systems that promote biodiversity and soil health.Overall, incorporating alternative feeds into livestock diets can be a win-win situation for both the animals and the environment.
• Alternative feeds provide a more balanced and nutritious diet for livestock
• Improved overall health and well-being of the animals
• Better growth rates and reproductive performance
• Cost-effective option, especially when traditional feed sources are expensive or scarce
• Environmental benefits include reducing reliance on monoculture crops
• Minimizing environmental impact associated with intensive farming practices
• Promoting sustainable livestock production systems that promote biodiversity and soil health
In conclusion, utilizing alternative feeds in livestock diets not only benefits the animals by providing a more balanced diet but also has positive impacts on the environment. Farmers can improve their animals’ health and well-being while contributing to sustainable agricultural practices.
Understanding the Nutritional Needs of Livestock
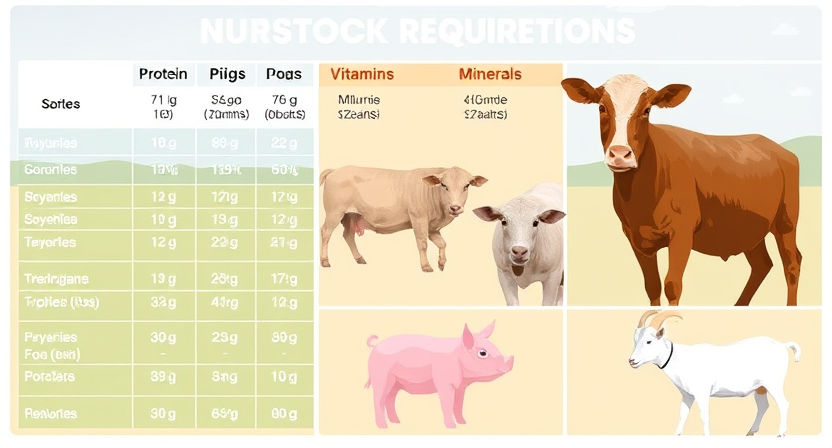
Livestock have diverse nutritional requirements that must be met to ensure their optimal health and productivity. These needs vary depending on the species, age, weight, and stage of production. For example, growing animals require higher levels of protein and energy to support their rapid development, while lactating or gestating animals have increased requirements for certain nutrients to support the production of milk or the growth of offspring. Understanding these specific nutritional needs is crucial for formulating balanced diets that promote overall well-being and performance in livestock.
In addition to protein and energy, livestock also require essential vitamins, minerals, and water for proper growth and functioning. These micronutrients play vital roles in metabolic processes, immune function, bone development, and overall health maintenance. Deficiencies or imbalances in these nutrients can lead to various health issues, decreased fertility, and suboptimal production levels. By comprehensively understanding the nutritional needs of livestock and formulating diets that meet these requirements, farmers can support the health, longevity, and productivity of their animals.
• Livestock have diverse nutritional requirements based on species, age, weight, and stage of production
• Growing animals need higher levels of protein and energy for rapid development
• Lactating or gestating animals require increased nutrients to support milk production or offspring growth
• Essential vitamins, minerals, and water are also necessary for proper growth and functioning
• Micronutrients play crucial roles in metabolic processes, immune function, bone development, and overall health maintenance
• Deficiencies in nutrients can lead to health issues, decreased fertility, and suboptimal production levels
Grasses and Forages as Feed Alternatives

Grasses and forages are vital components of livestock diets, providing essential nutrients for their growth and overall well-being. These natural feed alternatives are rich in fiber, which aids in digestion and helps maintain a healthy gut environment for the animals. Furthermore, grasses and forages offer a cost-effective way to supplement the nutritional requirements of livestock, particularly in grazing-based production systems.
Incorporating a variety of grasses and forages into livestock diets can enhance the diversity of nutrients available to the animals, promoting better overall health and performance. Different types of grasses and forages offer varying levels of protein, energy, and minerals, allowing farmers to customize feed options based on the specific needs of their livestock. By utilizing grasses and forages as feed alternatives, farmers can also reduce reliance on processed feeds, leading to potential cost savings and a more sustainable approach to animal nutrition.
• Grasses and forages are essential for livestock diets, providing vital nutrients for growth and well-being
• Rich in fiber, aiding digestion and maintaining a healthy gut environment
• Cost-effective way to supplement nutritional requirements, especially in grazing-based systems
• Enhance nutrient diversity by incorporating a variety of grasses and forages into diets
• Customizable feed options based on specific livestock needs, such as protein, energy, and minerals
• Reduce reliance on processed feeds by utilizing grasses and forages as alternatives
• Potential cost savings and more sustainable approach to animal nutrition
Silage and Haylage for Livestock Nutrition

Silage and haylage are popular feed options for livestock, especially during times when fresh forage is not readily available. Silage is fermented forage that is stored in airtight conditions, while haylage is fermented grass or legume forage with a higher moisture content than hay. These preserved feeds provide essential nutrients to animals, ensuring their health and productivity throughout the year.
The fermentation process used to make silage and haylage helps preserve nutrients and maintain feed quality for extended periods. This is particularly beneficial during the winter months or in regions where fodder is scarce. Livestock fed with silage and haylage tend to have consistent access to a balanced diet, promoting overall well-being and steady growth.
• Silage and haylage are popular feed options for livestock
• Silage is fermented forage stored in airtight conditions
• Haylage is fermented grass or legume forage with higher moisture content than hay
• Preserved feeds provide essential nutrients to animals throughout the year
The fermentation process plays a crucial role in preserving nutrients and maintaining feed quality. This ensures that livestock have access to high-quality nutrition even when fresh forage is not available. By feeding silage and haylage, farmers can help their animals stay healthy and productive, ultimately leading to better growth rates and overall well-being. Additionally, these preserved feeds offer a convenient way to store excess forage during peak growing seasons for later use when resources are limited.
Root Vegetables and Tubers as Feed Sources
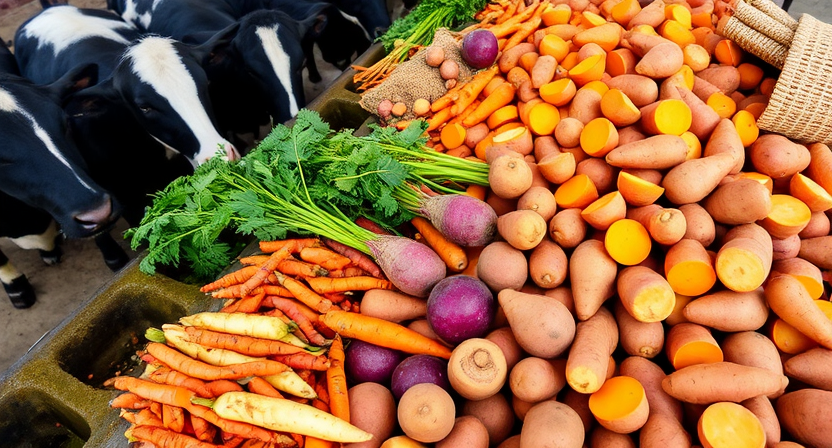

Root vegetables and tubers can serve as valuable feed sources for livestock due to their high nutrient content and energy-providing qualities. Carrots, beets, sweet potatoes, and turnips are all examples of root vegetables that can be incorporated into the diet of animals such as cattle, sheep, and pigs. These vegetables are not only rich in essential vitamins and minerals but also provide a good source of carbohydrates for energy production in livestock.
Additionally, tubers like potatoes and yams offer a starchy component to the animal’s diet, helping to maintain their energy levels and overall health. By including a variety of root vegetables and tubers in the feed regimen, livestock owners can ensure that their animals receive a diverse range of nutrients necessary for optimal growth and performance. It is important to consider the appropriate quantity and preparation of these feed sources to avoid any negative impacts on the animals’ digestive health.
• Root vegetables and tubers are high in nutrients and provide energy for livestock
• Examples include carrots, beets, sweet potatoes, turnips, potatoes, and yams
• These vegetables offer essential vitamins, minerals, and carbohydrates for animals’ diets
• Including a variety of root vegetables and tubers can ensure optimal growth and performance in livestock
• Quantity and preparation of feed sources should be considered to maintain digestive health in animals
Legumes as Protein-Rich Feed Alternatives

Legumes are a valuable source of protein for livestock, providing essential amino acids necessary for growth and maintenance. Examples of legumes commonly used as feed alternatives include alfalfa, clover, soybeans, and peas. These protein-rich legumes not only contribute to meeting the dietary needs of animals but also aid in enhancing overall health and productivity.
The protein content in legumes can vary depending on the type and maturity of the plants. Proper harvesting and storage methods are crucial to preserve the nutritional value of legumes as feed alternatives. In addition to their protein content, legumes also offer other beneficial nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and fiber, making them a versatile and valuable component of a balanced diet for livestock.
• Legumes are a valuable source of protein for livestock
• Examples include alfalfa, clover, soybeans, and peas
• Essential amino acids necessary for growth and maintenance are provided by legumes
• Proper harvesting and storage methods are crucial to preserve nutritional value
• In addition to protein, legumes offer vitamins, minerals, and fiber
Fruits and Vegetables for Livestock Nutrition
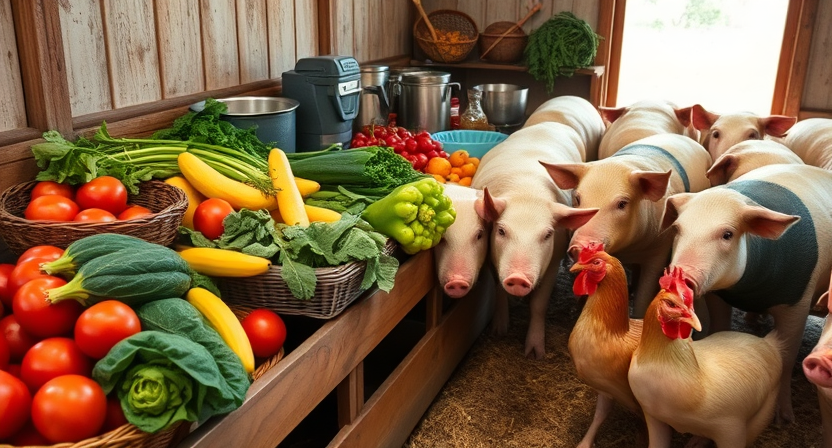

Fruits and vegetables can be valuable additions to a livestock’s diet, providing essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. These natural sources of nutrients can enhance the overall health and well-being of animals, promoting optimal growth and productivity. Farmers can consider incorporating a variety of fruits such as apples, bananas, and berries, as well as vegetables like carrots, beets, and leafy greens into their livestock feed to offer a diverse range of benefits.
Incorporating fruits and vegetables into livestock nutrition can also be a sustainable practice, utilizing surplus or imperfect produce that may otherwise go to waste. By repurposing these items as feed alternatives, farmers can reduce food waste while providing their animals with a nutritious and varied diet. Additionally, the high water content in many fruits and vegetables can help keep livestock hydrated, especially during hot weather or periods of increased activity.
• Fruits and vegetables can provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber to livestock
• Including a variety of fruits such as apples, bananas, and berries, as well as vegetables like carrots, beets, and leafy greens can offer diverse benefits
• Incorporating surplus or imperfect produce into livestock feed can help reduce food waste
• High water content in many fruits and vegetables can help keep livestock hydrated
• Utilizing fruits and vegetables in livestock nutrition promotes optimal growth and productivity
Grains and Seeds as Feed Options
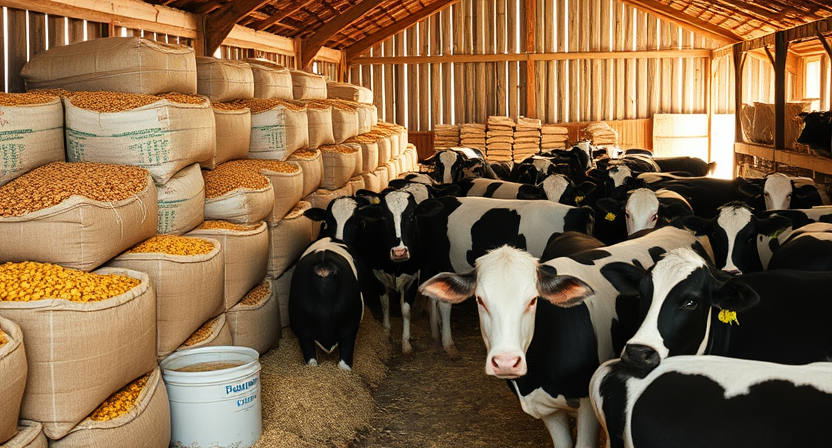

Grains and seeds are essential feed options for livestock, providing a rich source of carbohydrates, proteins, and essential nutrients. Corn, barley, oats, and wheat are commonly used grains that can be fed whole or processed into different forms such as pellets or meal for easier consumption by animals. These grains are not only energy-dense but also contribute to the overall health and growth of livestock when incorporated into their diets.
In addition to grains, seeds like soybeans, sunflower seeds, and flaxseeds are valuable feed options for livestock due to their high protein content and essential fatty acids. These seeds can be included in the animal’s diet as whole seeds or as meal after processing. Providing a balance of grains and seeds in the livestock’s diet can help meet their nutritional requirements and promote optimal health and productivity.
• Grains and seeds are essential feed options for livestock
• Common grains include corn, barley, oats, and wheat
• Grains can be fed whole or processed into pellets or meal
• Seeds like soybeans, sunflower seeds, and flaxseeds are high in protein and essential fatty acids
• Balancing grains and seeds in the diet promotes optimal health and productivity
Herbs and Spices for Livestock Health

Herbs and spices are not only flavorful additions to our meals but can also play a significant role in promoting the health of livestock. Certain herbs like oregano, thyme, and garlic have been found to possess natural antimicrobial properties, helping to support the immune system of animals. Spices such as cinnamon and turmeric are known for their anti-inflammatory effects, which can aid in reducing the risk of inflammation-related diseases in livestock.
Additionally, herbs and spices can act as natural insect repellents, helping to protect animals from pesky pests and parasites. Plants like mint, basil, and lavender have been shown to deter insects, minimizing the need for chemical interventions that can be harmful to both animals and the environment. By incorporating a variety of herbs and spices into the diet of livestock, farmers can not only enhance the flavor of the feed but also boost the overall health and well-being of their animals.
• Oregano, thyme, and garlic possess natural antimicrobial properties
• Cinnamon and turmeric have anti-inflammatory effects
• Mint, basil, and lavender act as natural insect repellents
By incorporating these herbs and spices into the diet of livestock, farmers can improve the health and well-being of their animals while also reducing the need for chemical interventions. This holistic approach to animal care not only benefits the livestock but also promotes sustainable farming practices that are better for both animals and the environment.
Nutritional Supplements for Livestock

Nutritional supplements can play a crucial role in meeting the specific dietary requirements of livestock. These supplements are formulated to address potential nutritional deficiencies in the animal’s diet, ensuring optimal health and performance. Commonly used supplements include minerals like calcium, phosphorus, and selenium, as well as vitamins such as A, D, and E. By incorporating these supplements into the livestock’s feed regimen, farmers can support growth, reproduction, and overall well-being.
It is essential for livestock farmers to consult with veterinary professionals or animal nutritionists when considering the use of nutritional supplements. These experts can provide guidance on selecting the most appropriate supplements based on the specific needs of the animals and the existing diet. Additionally, they can offer advice on proper dosages to avoid over-supplementation, which can have negative effects on animal health. Ultimately, incorporating nutritional supplements thoughtfully and strategically can contribute to the overall health and productivity of livestock.
• Nutritional supplements address potential deficiencies in livestock diets
• Common supplements include minerals like calcium, phosphorus, and selenium
• Vitamins such as A, D, and E are also commonly used
• Supplements support growth, reproduction, and overall well-being of livestock
It is crucial for farmers to seek guidance from veterinary professionals or animal nutritionists when considering nutritional supplements for their livestock. These experts can help choose the right supplements based on specific needs and existing diet. They can also advise on proper dosages to prevent over-supplementation. Thoughtful incorporation of supplements can enhance the health and productivity of livestock in the long run.
Probiotics and Prebiotics for Gut Health

Probiotics are live microorganisms that provide health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. These beneficial bacteria help maintain a healthy balance in the gut by promoting digestion and nutrient absorption. By populating the intestines with good bacteria, probiotics can enhance the overall well-being of livestock and support their immune system.
Prebiotics, on the other hand, are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for beneficial bacteria in the gut. They help stimulate the growth and activity of probiotics, leading to improved gut health and digestion in livestock. Including prebiotics in the feed regimen can help optimize nutrient utilization and support a healthy microbiome in the digestive tract of animals.
• Probiotics are essential for maintaining a healthy balance in the gut
• They promote digestion and nutrient absorption in livestock
• Prebiotics serve as food for beneficial bacteria in the gut
• Including prebiotics in feed can improve gut health and digestion
• Both probiotics and prebiotics work together to support a healthy microbiome
Molasses and Sweeteners as Feed Additives

Molasses and sweeteners are commonly used as feed additives for livestock to enhance palatability and provide a concentrated source of energy. Molasses, a by-product of sugar production, is a rich source of essential minerals such as iron, potassium, and calcium. Its sticky texture helps bind other feed ingredients together, making it easier for animals to consume their feed efficiently.
Sweeteners, such as sugar beet pulp or high-fructose corn syrup, can also be utilized in livestock feed to improve taste and increase energy content. These additives are especially beneficial for picky eaters or animals with high energy requirements, such as lactating cows or growing pigs. When used in moderation as part of a balanced diet, molasses and sweeteners can contribute to overall livestock health and performance.
• Molasses is a rich source of essential minerals such as iron, potassium, and calcium
• The sticky texture of molasses helps bind other feed ingredients together
• Sweeteners like sugar beet pulp or high-fructose corn syrup can improve taste and increase energy content in livestock feed
• These additives are beneficial for picky eaters or animals with high energy requirements
• When used in moderation as part of a balanced diet, molasses and sweeteners can contribute to overall livestock health and performance
Minerals and Vitamins for Livestock Well-Being

When it comes to ensuring the well-being of livestock, providing adequate minerals and vitamins in their diet is essential. Minerals play a crucial role in various bodily functions, such as bone development, muscle function, and nerve transmission. The most common essential minerals for livestock include calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, potassium, and sulfur. These minerals are typically found in feed sources like forages, grains, and mineral supplements.
In addition to minerals, vitamins are also vital for the overall health of livestock. Vitamins are important for the proper functioning of various metabolic processes and immune system functions. Some key vitamins for livestock include Vitamin A, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, and the B-complex vitamins. These vitamins can be sourced from fresh forages, grains, and commercial vitamin supplements. Providing a balanced diet that includes a variety of minerals and vitamins is crucial for promoting optimal health and well-being in livestock.
• Calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, potassium, and sulfur are essential minerals for livestock
• Minerals play a crucial role in bone development, muscle function, and nerve transmission
• These minerals can be found in feed sources like forages, grains, and mineral supplements
• Vitamin A, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, and B-complex vitamins are important for livestock health
• Vitamins are necessary for metabolic processes and immune system functions
• Fresh forages, grains, and commercial vitamin supplements are sources of key vitamins
Providing a balanced diet that includes a variety of minerals and vitamins is crucial for promoting optimal health and well-being in livestock. Livestock owners should work with veterinarians or nutritionists to ensure that their animals receive the proper nutrients needed to thrive. By paying attention to mineral and vitamin intake in livestock diets, farmers can help prevent deficiencies or imbalances that may negatively impact animal health. Ultimately,
investing in the nutritional needs of livestock can lead to improved productivity,
reproduction rates,and overall well-being of the animals.
Feeding Livestock Kitchen Scraps
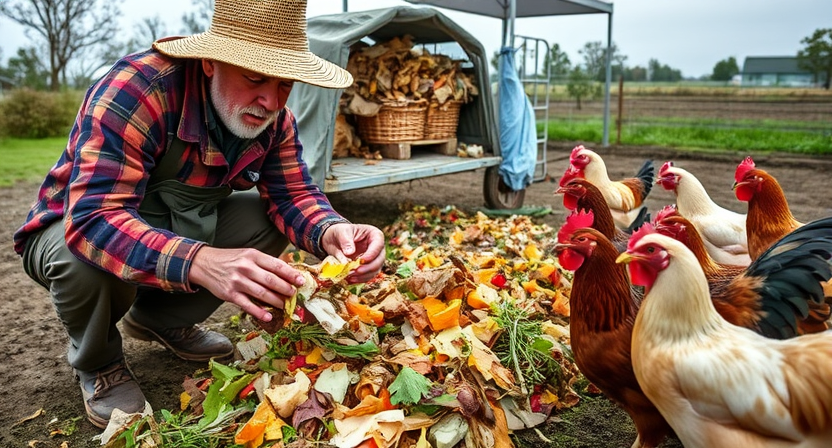

Livestock can benefit from kitchen scraps that would otherwise go to waste. Leftover fruits, vegetables, and grains can serve as nutritious additions to the diet of animals such as pigs, chickens, and goats. While providing kitchen scraps can help reduce food waste, it is important to ensure that the scraps are safe and suitable for consumption by the livestock. Avoid feeding animals scraps that are spoiled, moldy, or potentially harmful to their health.
Feeding livestock kitchen scraps can also be a cost-effective way to supplement their diet with additional nutrients. By incorporating a variety of scraps into their feeding regimen, farmers can introduce new flavors and textures to the animals’ diet, enriching their overall eating experience. However, it is crucial to monitor the quantity and types of scraps provided to prevent overfeeding or imbalance in their nutritional intake.
• Livestock can benefit from kitchen scraps that would otherwise go to waste
• Leftover fruits, vegetables, and grains can serve as nutritious additions to the diet of animals such as pigs, chickens, and goats
• Ensure that the scraps are safe and suitable for consumption by the livestock
• Avoid feeding animals scraps that are spoiled, moldy, or potentially harmful to their health
Feeding livestock kitchen scraps can also be a cost-effective way to supplement their diet with additional nutrients. By incorporating a variety of scraps into their feeding regimen, farmers can introduce new flavors and textures to the animals’ diet, enriching their overall eating experience. However, it is crucial to monitor the quantity and types of scraps provided to prevent overfeeding or imbalance in their nutritional intake.
Utilizing Crop Residues as Feed Alternatives
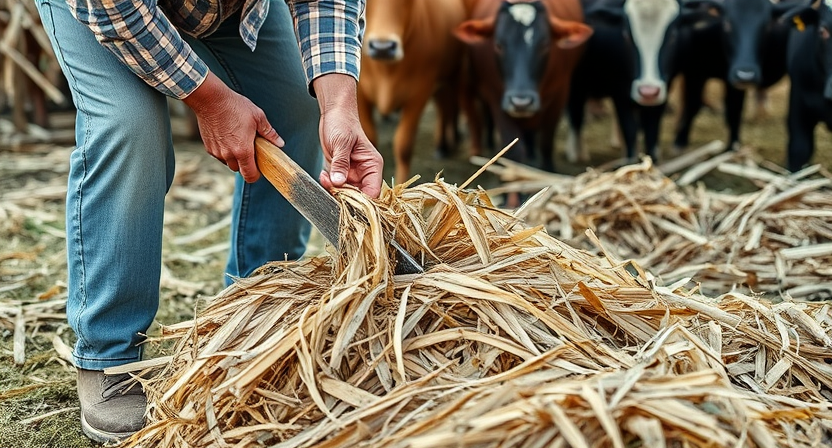

Crop residues can be a valuable resource for providing additional feed options for livestock. After the main harvest, residues such as corn stover, wheat straw, and rice hulls can be utilized to supplement the animals’ diet. These materials can offer fiber, energy, and some nutrients, helping to diversify the feed sources available for the livestock.
When incorporating crop residues into the feeding regimen, it is essential to consider factors like the nutritional content, digestibility, and any potential harmful substances. Some residues may require processing methods such as chopping or grinding to enhance digestibility and make them more palatable for the animals. By properly managing and utilizing crop residues, livestock owners can maximize the use of their resources and provide a well-rounded diet for their animals.
• Crop residues such as corn stover, wheat straw, and rice hulls can be used as feed alternatives
• These materials provide fiber, energy, and some nutrients for livestock
• Factors to consider when incorporating crop residues include nutritional content, digestibility, and potential harmful substances
• Processing methods like chopping or grinding may be necessary to enhance digestibility and palatability
• Proper management of crop residues can help maximize resources and provide a well-rounded diet for animals
Feeding Livestock with By-Products
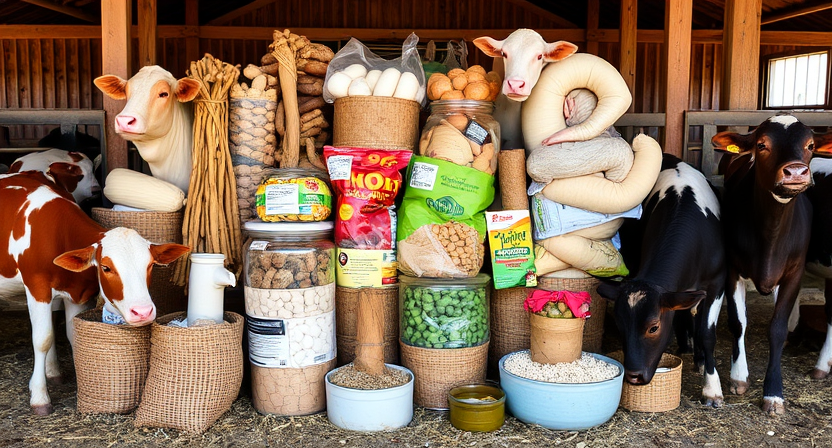

When it comes to feeding livestock, utilizing by-products from various industries can be a cost-effective and sustainable option. By-products refer to materials that are leftover or produced as a co-product during the manufacturing process of goods. These materials, which may include items like brewers’ grains, citrus pulp, and distillers grains, can serve as valuable sources of nutrients for livestock diets. Incorporating these by-products into feed rations not only helps reduce waste but also provides an alternative feed source that can diversify the nutritional profile of the animals’ diet.
Using by-products in livestock feed formulations requires careful consideration of their nutritional content and how they can complement the existing diet. It is essential to assess the digestibility, energy content, protein levels, and potential presence of any anti-nutritional factors in these by-products to ensure they are suitable for the animals’ consumption. Moreover, working closely with a nutritionist or veterinarian can help tailor the inclusion of by-products in the feed program to meet the specific needs and production goals of the livestock enterprise.
• By-products from various industries can be a cost-effective option for feeding livestock
• Materials like brewers’ grains, citrus pulp, and distillers grains are valuable sources of nutrients
• Incorporating by-products into feed rations helps reduce waste and diversify the animals’ diet
• Nutritional content, digestibility, energy levels, protein content, and anti-nutritional factors should be considered when using by-products in feed formulations
• Working with a nutritionist or veterinarian can help tailor the inclusion of by-products to meet specific needs and production goals
Balancing Homemade Feeds for Livestock
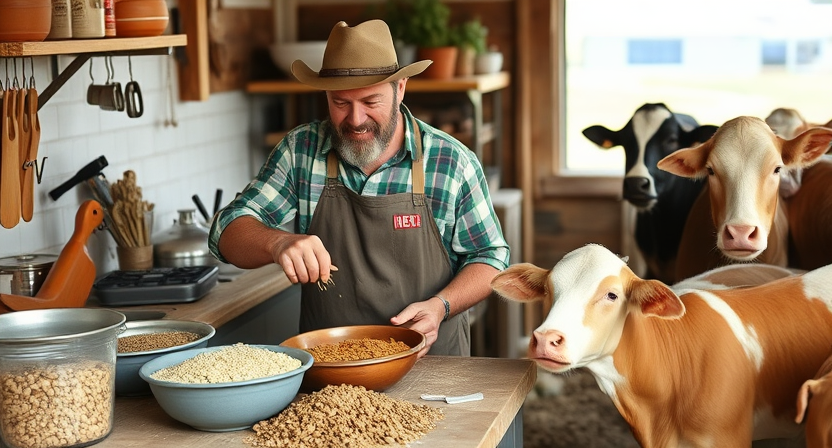

Homemade feeds can be a cost-effective way to provide nutrition to livestock while allowing for more control over ingredients. However, it is crucial to ensure that these feeds are properly balanced to meet the specific nutritional needs of the animals. One key aspect of balancing homemade feeds is to consider the protein, energy, fiber, mineral, and vitamin content required by the livestock at different stages of growth or production.
To achieve a balanced homemade feed, it is essential to have a good understanding of the nutrient requirements of the particular species of livestock being fed. This involves consulting nutritional guidelines or working with a veterinarian or animal nutritionist to formulate a feed ration that provides the necessary nutrients in the right proportions. Additionally, regular monitoring of the animals’ health, growth, and performance can help assess the effectiveness of the homemade feed and make any necessary adjustments to ensure optimal nutrition.
• Homemade feeds can be cost-effective and provide more control over ingredients
• Properly balancing homemade feeds is crucial to meet specific nutritional needs of livestock
• Consider protein, energy, fiber, mineral, and vitamin content for different growth stages or production
• Understand nutrient requirements of the particular species of livestock being fed
• Consult nutritional guidelines or work with a veterinarian or animal nutritionist for formulation
• Regular monitoring of animals’ health, growth, and performance is essential
• Make necessary adjustments to homemade feed to ensure optimal nutrition
Feeding Livestock in Seasonal Changes

As the seasons shift, it is crucial for livestock farmers to adapt their feeding practices to meet the changing nutritional needs of their animals. During the colder months, animals may require more energy to maintain their body temperature, leading to a greater need for high-quality forages and calorie-dense feeds. Conversely, in the warmer months, providing ample access to fresh pasture and ensuring proper hydration becomes pivotal for optimal livestock health and performance.
It is essential for farmers to closely monitor their livestock’s body condition and adjust their feeding regimen accordingly as the seasons progress. By carefully assessing the available feed resources and understanding the changing nutritional requirements of their animals, farmers can effectively navigate the challenges posed by seasonal changes and promote the overall well-being of their livestock.
• During the colder months, animals may require more energy to maintain body temperature
• High-quality forages and calorie-dense feeds are essential during this time
• In warmer months, providing ample access to fresh pasture and ensuring proper hydration is crucial
• Farmers should closely monitor livestock’s body condition and adjust feeding regimen accordingly
• Assessing available feed resources and understanding changing nutritional requirements is key
• Effective navigation of challenges posed by seasonal changes promotes overall well-being of livestock.
Tips for Transitioning to Natural Feeding Practices

As you begin transitioning to natural feeding practices for your livestock, it is important to start gradually. Sudden changes in diet can lead to digestive upset in animals. Introduce new feed options slowly, allowing animals time to adapt to the different nutritional content.
Monitoring your livestock’s health during the transition period is crucial. Keep a close eye on their body condition, behavior, and overall well-being. If you notice any signs of distress or changes in their health, adjust the feeding regimen accordingly. Consulting with a veterinarian or livestock nutritionist can also provide valuable guidance during this process.
• Start gradually when transitioning to natural feeding practices
• Introduce new feed options slowly to allow animals time to adapt
• Monitor livestock’s health closely during the transition period
• Keep an eye on body condition, behavior, and overall well-being
• Adjust feeding regimen if signs of distress or changes in health occur
• Consult with a veterinarian or livestock nutritionist for guidance




