Vaccines and Health Care for Farm Animals
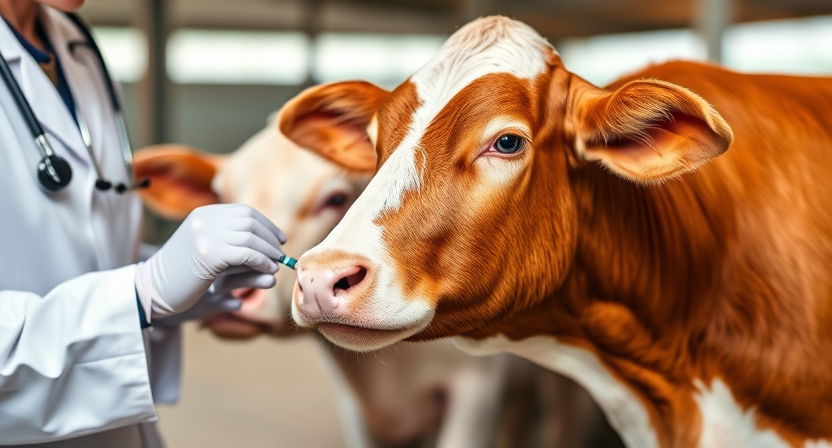

Vaccination Schedule for Farm Animals

Vaccinations play a crucial role in maintaining the health and well-being of farm animals. Each species of farm animal has specific vaccination requirements based on their susceptibility to certain diseases and the prevalence of those diseases in their environment. Understanding the recommended vaccination schedule for your farm animals is essential in preventing outbreaks and ensuring a healthy herd or flock.
For example, common vaccinations for cattle often include protection against diseases like blackleg, infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, and bovine viral diarrhea. On the other hand, poultry vaccinations may target diseases such as Newcastle disease and infectious bronchitis. By following the appropriate vaccination schedule for each species of farm animal, farmers can help safeguard their animals from preventable illnesses and minimize the risk of disease transmission within their operation.
• Vaccinations are essential for maintaining the health of farm animals
• Each species of farm animal has specific vaccination requirements
• Understanding the recommended vaccination schedule is crucial for preventing outbreaks
• Common vaccinations for cattle include protection against diseases like blackleg and infectious bovine rhinotracheitis
• Poultry vaccinations may target diseases such as Newcastle disease and infectious bronchitis
Common Diseases in Farm Animals

Farm animals are susceptible to a wide range of common diseases that can impact their health and productivity. Respiratory infections, such as pneumonia, are frequently seen in farm animals, especially in crowded or poorly ventilated environments. These infections can be caused by various pathogens, including bacteria and viruses, and often present with symptoms like coughing, nasal discharge, and difficulty breathing.
Another common health issue in farm animals is gastrointestinal problems, such as diarrhea. This can be caused by infections, parasites, or dietary indiscretions, and can quickly lead to dehydration and weight loss if not addressed promptly. Farm owners should be vigilant in monitoring their animals for signs of gastrointestinal issues and seek veterinary assistance if necessary.
• Respiratory infections, such as pneumonia, are common in farm animals
• Symptoms include coughing, nasal discharge, and difficulty breathing
• Caused by bacteria and viruses
• Gastrointestinal problems like diarrhea are also prevalent in farm animals
• Can be caused by infections, parasites, or dietary indiscretions
• Can lead to dehydration and weight loss if not treated promptly
• Owners should monitor for signs of gastrointestinal issues and seek veterinary help when needed.
Importance of Preventative Health Care

Preventative health care is a crucial aspect of ensuring the well-being and productivity of farm animals. By implementing regular vaccinations, deworming, and proper nutrition, farmers can significantly reduce the risk of diseases and maintain the overall health of their livestock. Preventative measures not only help in preventing illnesses but also contribute to the sustainability of the farm operation by minimizing the need for costly treatments and interventions.
Regular veterinary exams play a key role in preventative health care for farm animals. These exams allow for early detection of any potential health issues, enabling prompt intervention and treatment. Additionally, veterinarians can provide valuable guidance on biosecurity measures, parasite control, and vaccination protocols tailored to the specific needs of each farm animal species. Investing in preventative health care ultimately leads to healthier and more resilient animals, which in turn supports the long-term success of the farm.
• Regular vaccinations, deworming, and proper nutrition are essential for maintaining livestock health
• Preventative measures reduce the risk of diseases and minimize the need for costly treatments
• Veterinary exams allow for early detection of health issues and tailored guidance on biosecurity measures
Signs of Illness in Farm Animals

Recognizing signs of illness in farm animals is crucial for timely intervention and preventing the spread of disease within the herd or flock. Some common indicators of ill health in farm animals include changes in behavior, such as lethargy, isolation from the group, or aggression towards other animals. Additionally, a decrease in appetite or water intake, as well as weight loss, can be red flags that something is amiss with an animal’s health.
Physical symptoms may also manifest in farm animals showing signs of illness. These can include abnormal discharges from the eyes, nose, or mouth, as well as coughing, sneezing, or difficulty breathing. Changes in posture, gait, or movement patterns may also signal an underlying health issue that requires veterinary attention. Familiarizing oneself with these signs can empower farmers and caretakers to act promptly in safeguarding the health and well-being of their farm animals.
• Changes in behavior such as lethargy, isolation from the group, or aggression towards other animals
• Decrease in appetite or water intake
• Weight loss
Physical symptoms to watch for include:
• Abnormal discharges from eyes, nose, or mouth
• Coughing, sneezing, or difficulty breathing
• Changes in posture, gait, or movement patterns
Recognizing these signs early on can help prevent the spread of disease and ensure that farm animals receive the necessary care and treatment they need. It is important for farmers and caretakers to stay vigilant and observant when it comes to monitoring the health of their livestock. Regular check-ups by a veterinarian can also help catch any potential issues before they escalate into more serious problems. By being proactive and attentive to signs of illness in farm animals, farmers can maintain a healthy herd or flock and promote overall animal welfare on their farms.
Biosecurity Measures for Disease Prevention

Biosecurity measures are essential for preventing the introduction and spread of diseases in farm animals. One key aspect is controlling and monitoring the movement of animals onto the farm. Implementing strict biosecurity protocols such as isolating new animals upon arrival, conducting health screenings, and ensuring proper quarantine measures can significantly reduce the risk of disease transmission within the herd.
Additionally, maintaining a clean and sanitized environment is crucial for disease prevention. Regularly cleaning and disinfecting shared spaces, equipment, and water sources can help eliminate potential sources of infection. By practicing good hygiene and biosecurity measures, farmers can protect the health and well-being of their animals and prevent the devastating effects of infectious diseases on their operations.
• Isolating new animals upon arrival
• Conducting health screenings
• Ensuring proper quarantine measures
• Regularly cleaning and disinfecting shared spaces, equipment, and water sources
Proper Nutrition for Farm Animals

Farm animals require a balanced diet to support their growth, reproduction, and overall health. The nutritional needs of animals can vary depending on their species, age, and purpose. It is essential to provide farm animals with high-quality feed that meets their specific dietary requirements. Adequate protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals are crucial for maintaining optimal health and productivity in farm animals.
Proper nutrition plays a critical role in preventing diseases and improving the immune system of farm animals. Deficiencies in essential nutrients can weaken the animals’ immune response, making them more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Additionally, inadequate nutrition can result in poor growth, reproductive problems, and decreased milk or meat production. Farmers should work closely with veterinarians or animal nutritionists to develop a customized feeding program that meets the specific needs of their animals.
• Farm animals require a balanced diet for growth, reproduction, and overall health
• Nutritional needs vary by species, age, and purpose
• High-quality feed is essential to meet specific dietary requirements
• Adequate protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals are crucial for optimal health and productivity
Proper nutrition is key in preventing diseases and boosting the immune system of farm animals. Deficiencies in essential nutrients can compromise their immune response and make them more vulnerable to infections. Inadequate nutrition can also lead to stunted growth, reproductive issues, and reduced milk or meat production. Collaborating with veterinarians or animal nutritionists can help farmers create a personalized feeding plan tailored to their animals’ unique needs.
Farmers must prioritize providing their livestock with the necessary nutrients through high-quality feed sources. By ensuring that farm animals receive proper nutrition tailored to their individual requirements, farmers can promote optimal health outcomes and maximize productivity on their farms.
Housing and Environment Considerations

Farm animals require proper housing and environmental conditions to thrive. The housing should provide adequate space for the animals to move around comfortably and to exhibit natural behaviors. It is important to ensure good ventilation to prevent respiratory issues and to maintain optimal temperature levels to promote animal health. Additionally, the housing should be constructed with materials that are easy to clean and disinfect to prevent the spread of diseases.
The environment in which farm animals are kept also plays a crucial role in their overall well-being. It is essential to provide clean bedding and regularly remove waste to prevent the buildup of bacteria and parasites. Access to clean water is vital for hydration and proper digestion. Moreover, natural light and outdoor access, when suitable, can contribute to the animals’ mental and physical health. Overall, maintaining a clean, comfortable, and safe housing and environment for farm animals is essential for their welfare and productivity.
• Proper housing is crucial for farm animals to thrive
• Adequate space should be provided for movement and natural behaviors
• Good ventilation is necessary to prevent respiratory issues
• Optimal temperature levels should be maintained for animal health
• Housing materials should be easy to clean and disinfect
• Clean bedding and waste removal are important for preventing bacteria and parasites
• Access to clean water is vital for hydration and digestion
• Natural light and outdoor access can benefit mental and physical health
• Maintaining a clean, comfortable, and safe environment is essential for animal welfare
Parasite Control for Farm Animals

Parasites can wreak havoc on farm animals, compromising their health and impacting productivity. It is crucial for farmers to implement effective parasite control strategies to protect the well-being of their livestock. Regular deworming of animals can help prevent infestations and keep parasites at bay. Various deworming medications are available, and it is important to consult with a veterinarian to determine the most suitable treatment based on the specific type of parasites prevalent in the region and the individual needs of the animals.
In addition to deworming, proper pasture management is essential in controlling parasites in farm animals. Rotational grazing, allowing pastures to rest, and removing manure promptly can all help reduce parasite burdens in the environment. By implementing a comprehensive parasite control program that includes both medicinal treatment and environmental management, farmers can significantly improve the overall health and welfare of their livestock, leading to better outcomes in terms of growth and production.
• Regular deworming of animals is crucial for preventing infestations
• Consult with a veterinarian to determine the most suitable treatment
• Proper pasture management is essential in controlling parasites
– Rotational grazing can help reduce parasite burdens
– Allowing pastures to rest can also be beneficial
– Removing manure promptly helps prevent parasite spread
• Implement a comprehensive parasite control program for better outcomes
Routine Veterinary Exams for Farm Animals
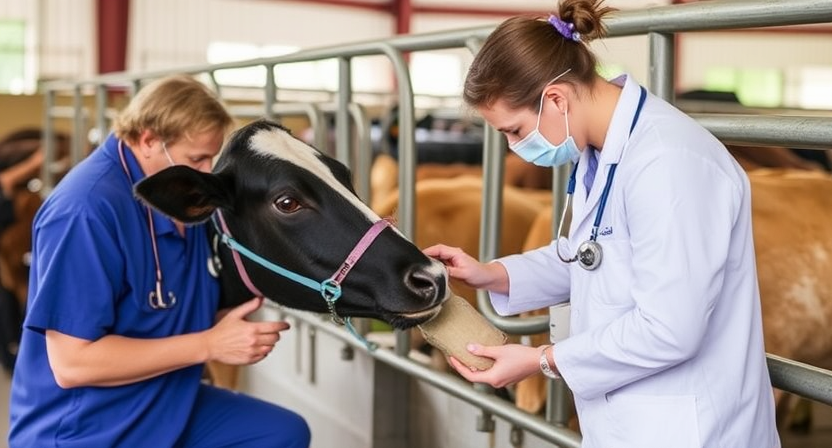

During routine veterinary exams for farm animals, the veterinarian will conduct a thorough physical examination to assess the overall health of the animal. This may include checking the animal’s weight, body condition, temperature, heart rate, and respiration rate. The vet will also examine the animal’s eyes, ears, nose, mouth, skin, and coat for any signs of abnormalities or health issues.
In addition to the physical exam, routine veterinary exams for farm animals may also involve preventive care measures such as vaccinations, deworming, and parasite control. The vet may recommend specific vaccinations based on the animal’s age, species, and individual health needs. Regular veterinary exams are essential for maintaining the health and well-being of farm animals, as they allow for early detection and treatment of any potential health problems.
• During routine veterinary exams for farm animals, the veterinarian will conduct a thorough physical examination
• The exam may include checking weight, body condition, temperature, heart rate, and respiration rate
• The vet will also examine eyes, ears, nose, mouth, skin, and coat for any signs of abnormalities or health issues
• Routine veterinary exams may involve preventive care measures such as vaccinations, deworming, and parasite control
• Specific vaccinations may be recommended based on age, species, and individual health needs
Vaccination Protocols for Different Species
When it comes to vaccination protocols for farm animals, it is essential to recognize that different species have varying requirements. For example, cattle commonly receive vaccines for diseases such as blackleg, infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, and bovine viral diarrhea. On the other hand, poultry like chickens and turkeys may require vaccinations for diseases such as Newcastle disease and infectious bronchitis.
Similarly, swine are often vaccinated against diseases like porcine circovirus and leptospirosis to maintain their health and productivity. Sheep and goats also have their own specific vaccination needs, such as protection against diseases like tetanus and clostridial infections. Understanding the unique vaccination protocols for each species is crucial in ensuring the overall well-being and disease prevention in farm animals.
• Cattle commonly receive vaccines for diseases such as blackleg, infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, and bovine viral diarrhea.
• Poultry like chickens and turkeys may require vaccinations for diseases such as Newcastle disease and infectious bronchitis.
• Swine are often vaccinated against diseases like porcine circovirus and leptospirosis to maintain their health and productivity.
• Sheep and goats have specific vaccination needs, such as protection against diseases like tetanus and clostridial infections.
Understanding these unique vaccination protocols for each species is crucial in ensuring the overall well-being and disease prevention in farm animals. It is important for farmers to work closely with veterinarians to develop a comprehensive vaccination plan that meets the specific needs of their livestock. By following recommended vaccination schedules and practices, farmers can help protect their animals from potentially devastating illnesses while also promoting a healthy environment on their farms.
Handling and Restraint Techniques for Veterinary Procedures
When it comes to veterinary procedures for farm animals, proper handling and restraint techniques are crucial for ensuring the safety of both the animal and the veterinary staff. Understanding the behavior of the specific species being treated is essential in effectively and safely restraining them.
Veterinarians and animal health professionals should be well-versed in utilizing appropriate equipment and techniques to safely restrain farm animals during procedures. This not only helps in reducing the risk of injury to the animal but also allows for a more efficient and successful veterinary intervention.
• Proper handling and restraint techniques are crucial for ensuring safety during veterinary procedures
• Understanding the behavior of the specific species being treated is essential
• Veterinarians should be well-versed in utilizing appropriate equipment and techniques
• Safe restraint reduces risk of injury to animals
• Efficient handling allows for successful veterinary intervention
Emergency Care for Farm Animals

When faced with an emergency situation involving farm animals, it is crucial to act swiftly and decisively to ensure the well-being of the animals. One important aspect of emergency care is to have a designated first aid kit specifically for farm animals readily available at all times. This kit should include essential items such as bandages, antiseptic solution, wound dressings, and any necessary medications prescribed by a veterinarian for common ailments or conditions.
In addition to having a well-equipped first aid kit, it is essential for farm owners or caretakers to be familiar with basic first aid techniques for farm animals. This includes knowing how to properly handle and restrain an injured animal, cleaning and dressing wounds, and recognizing signs of distress or pain. Seeking immediate veterinary assistance is crucial in emergency situations, and having a plan in place for transporting injured animals to a veterinary clinic or hospital is paramount for their timely care and recovery.
• Properly handle and restrain injured animals
• Clean and dress wounds effectively
• Recognize signs of distress or pain in farm animals
• Seek immediate veterinary assistance in emergency situations
• Have a plan for transporting injured animals to a veterinary clinic or hospital
Zoonotic Diseases and Farm Animals

Zoonotic diseases are those that can be transmitted from animals to humans, posing a potential health risk to individuals working closely with farm animals. It is imperative for farmers and veterinary professionals to be aware of zoonotic diseases and take necessary precautions to prevent transmission. Common zoonotic diseases in farm animals include brucellosis, leptospirosis, avian influenza, and Q fever.
Proper hygiene practices, such as handwashing after handling animals or their waste, wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, and regular cleaning and disinfection of animal living areas, are essential in reducing the risk of zoonotic disease transmission. Additionally, early detection of symptoms in both animals and humans is crucial for timely treatment and containment of zoonotic diseases within farm settings.
• Proper hygiene practices, such as handwashing after handling animals or their waste
• Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment
• Regular cleaning and disinfection of animal living areas
• Early detection of symptoms in both animals and humans for timely treatment
Vaccination Side Effects and Risks
Vaccinations are a crucial tool in protecting farm animals from various diseases. While the benefits of vaccination outweigh the risks in most cases, it is important for farmers and veterinarians to be aware of potential side effects that can occur. Common side effects of vaccinations in farm animals may include mild fever, swelling at the injection site, or temporary lethargy.
In some rare instances, farm animals may experience more severe reactions to vaccines, such as allergic reactions or anaphylaxis. It is essential for farmers to closely monitor animals after vaccination and be prepared to seek veterinary care if any concerning symptoms arise. Additionally, understanding the potential risks associated with vaccines can help veterinarians make informed decisions when developing vaccination protocols for farm animals.
• Mild fever
• Swelling at the injection site
• Temporary lethargy
In rare instances, farm animals may experience:
• Allergic reactions
• Anaphylaxis
Farmers should:
– Monitor animals closely after vaccination
– Seek veterinary care if concerning symptoms arise
Veterinarians can:
– Make informed decisions when developing vaccination protocols
Health Certificates for Farm Animals

Health certificates for farm animals serve as important documentation to ensure the health and safety of the animals during transport or movement. These certificates are usually issued by a veterinarian after a thorough examination of the animals to verify their health status. They provide crucial information about the animal’s health condition, vaccinations, and any necessary treatments, which may be required for compliance with regulations or before entering specific markets or shows.
Health certificates are commonly required for the interstate or international movement of farm animals to prevent the spread of diseases. They help to demonstrate that the animals are free from infectious diseases and are fit for transport. Additionally, health certificates may also include details about the origin of the animals, their identification, and any specific health requirements mandated by the receiving party. It is essential for farmers and livestock owners to ensure that their animals have up-to-date health certificates when needed to facilitate smooth and safe transportation.
• Health certificates for farm animals are crucial documentation to ensure their health and safety during transport.
• These certificates are issued by veterinarians after a thorough examination of the animals to verify their health status.
• They provide information about the animal’s health condition, vaccinations, and any necessary treatments required for compliance with regulations.
• Health certificates are commonly required for interstate or international movement of farm animals to prevent disease spread.
• They demonstrate that the animals are free from infectious diseases and fit for transport.
• Certificates may also include details about the animal’s origin, identification, and specific health requirements mandated by receiving parties.
Vaccination Record Keeping
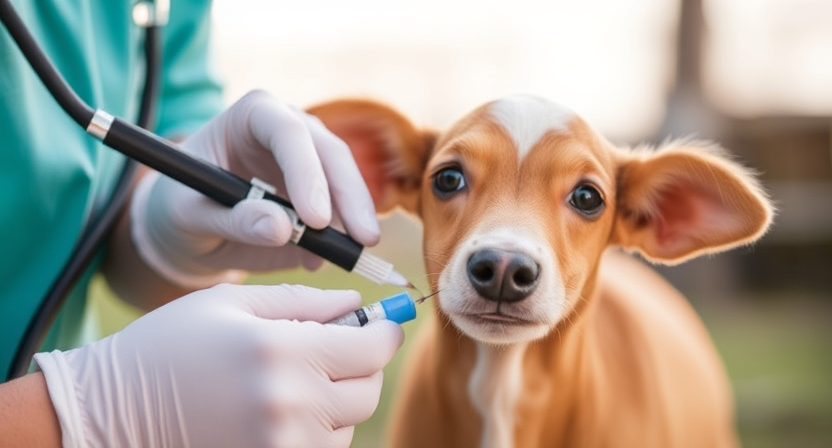

Proper vaccination record keeping is a crucial aspect of farm animal health management. Keeping detailed and accurate records of all vaccinations administered to each animal helps in ensuring that they receive the necessary vaccines at the appropriate times. This also aids in tracking the effectiveness of the vaccination program on the farm and assists in disease prevention strategies.
Maintaining vaccination records also plays a key role in complying with regulatory requirements and in demonstrating to veterinary professionals, inspectors, and potential buyers that the animals are up to date on their vaccinations. Clear and organized records make it easier to identify any gaps in vaccination coverage and allows for timely re-vaccination when needed. By prioritizing vaccination record keeping, farm owners and managers can effectively safeguard the health and well-being of their animals, as well as the overall success of their farming operations.
• Proper vaccination record keeping is essential for farm animal health management
• Detailed and accurate records ensure animals receive necessary vaccines at the right times
• Tracking effectiveness of vaccination program aids in disease prevention strategies
• Compliance with regulatory requirements is facilitated by maintaining vaccination records
• Clear and organized records make it easier to identify gaps in vaccination coverage
• Timely re-vaccination can be administered when needed
• Demonstrating up-to-date vaccinations to veterinary professionals, inspectors, and potential buyers is important for farm credibility
Alternative Health Care Options for Farm Animals
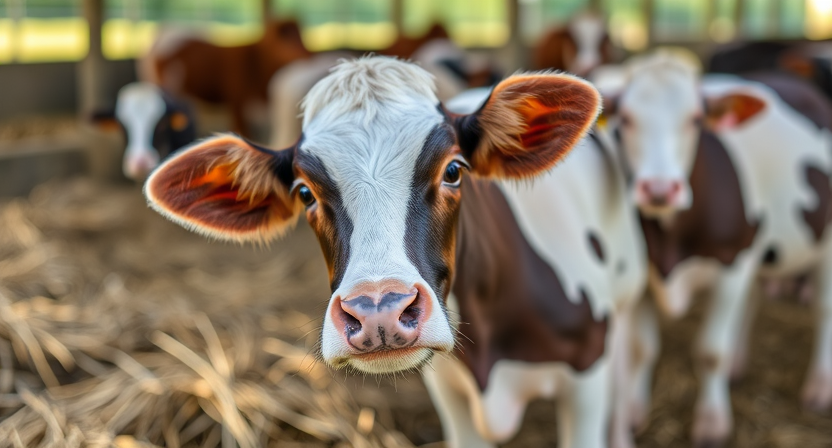

Alternative health care options for farm animals can provide complementary support to traditional veterinary care. Many farmers are exploring holistic treatments such as herbal remedies, acupuncture, and chiropractic adjustments to promote overall wellness in their livestock. These alternative therapies aim to address the root cause of health issues and improve the animal’s natural balance and resilience.
In addition to holistic treatments, some farmers are incorporating practices like aromatherapy, massage therapy, and nutritional supplements into their farm animal care routines. These alternative health care options can help reduce stress, improve immune function, and enhance the overall well-being of the animals. By combining traditional veterinary care with alternative therapies, farmers can offer a comprehensive approach to maintaining the health and vitality of their farm animals.
• Holistic treatments such as herbal remedies, acupuncture, and chiropractic adjustments can promote overall wellness in farm animals
• Alternative therapies aim to address the root cause of health issues and improve natural balance and resilience
• Aromatherapy, massage therapy, and nutritional supplements can help reduce stress, improve immune function, and enhance well-being in livestock
• Combining traditional veterinary care with alternative therapies offers a comprehensive approach to maintaining animal health
Supportive Care for Sick or Injured Farm Animals
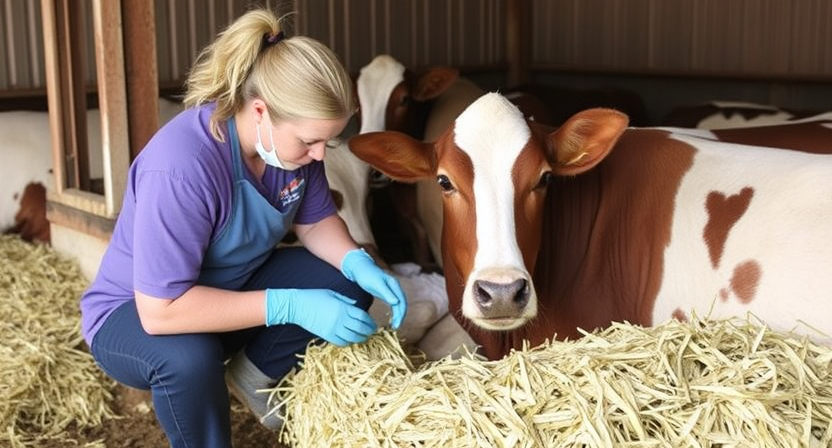

Providing supportive care for sick or injured farm animals is essential in promoting their recovery and well-being. When an animal is sick or injured, it is crucial to provide a comfortable and stress-free environment to aid in their healing process. This may involve isolating the affected animal to prevent the spread of disease and ensuring they have access to clean water, appropriate nutrition, and a quiet space to rest.
In addition to creating a conducive environment, administering proper medication, wound care, and other treatments as prescribed by a veterinarian are key aspects of supportive care. Monitoring the animal’s progress closely and addressing any changes in their condition promptly is vital in ensuring successful recovery. Additionally, providing emotional support and gentle handling can help reduce stress and promote a quicker return to health for the sick or injured farm animal.
• Providing a comfortable and stress-free environment is crucial for promoting recovery
• Isolating the affected animal to prevent disease spread is important
• Access to clean water, appropriate nutrition, and a quiet resting space are essential
• Administering proper medication, wound care, and treatments as prescribed by a veterinarian is key
• Monitoring the animal’s progress closely and addressing any changes promptly is vital
• Emotional support and gentle handling can help reduce stress and promote quicker recovery
Resources for Farm Animal Health Care

When it comes to caring for farm animals, having access to reliable resources is crucial for maintaining their health and well-being. Farmers and animal owners can benefit from a variety of sources such as veterinary clinics, agricultural extension services, and reputable online platforms that provide information on animal health and management practices. These resources can offer guidance on vaccination schedules, disease prevention strategies, proper nutrition, housing considerations, and other important aspects of farm animal care.
Additionally, joining local or online farming communities can be a valuable resource for exchanging knowledge and experiences with other farm animal owners. These communities provide a platform for farmers to seek advice, share tips, and learn from each other’s successes and challenges. By tapping into these resources, farmers can enhance their understanding of farm animal health care practices and improve the well-being of their animals.
• Veterinary clinics: These facilities provide professional guidance on animal health issues and offer services such as vaccinations, check-ups, and treatment for illnesses.
• Agricultural extension services: These organizations offer educational programs and resources to help farmers improve their farming practices, including information on livestock health care.
• Online platforms: Websites and forums dedicated to farm animal health provide a wealth of information on topics such as disease prevention, nutrition requirements, and best management practices.
• Farming communities: Joining local or online groups allows farmers to connect with others in the industry, share knowledge, seek advice, and learn from each other’s experiences.
Training and Education for Farm Animal Health Management
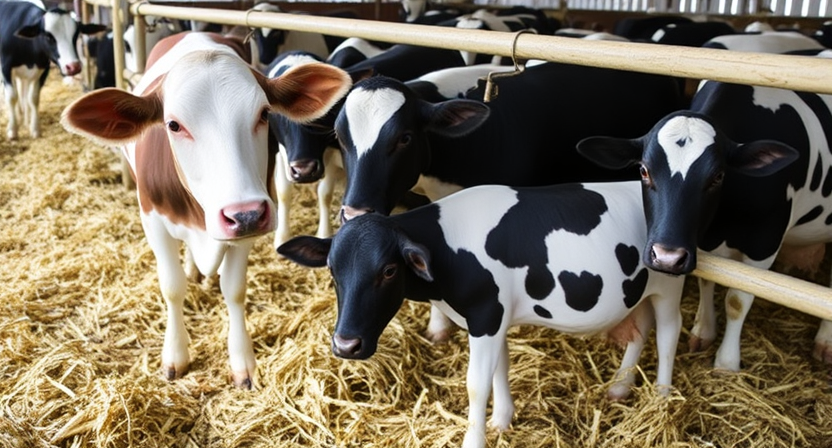

Training and education are essential components of farm animal health management. Farm owners and caretakers must stay informed about best practices, emerging diseases, and advancements in veterinary care to ensure the well-being of their animals. Regular training sessions and continuing education opportunities can help individuals develop the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively care for farm animals. By investing in training and education, farmers can improve their ability to recognize signs of illness, administer medications correctly, and implement biosecurity measures to prevent disease outbreaks.
Hands-on training experiences, workshops, webinars, and conferences offer valuable learning opportunities for individuals involved in farm animal health management. These educational activities provide a platform for farmers to interact with experts, share experiences, and gain insights into new technologies and practices that can enhance the health and welfare of their animals. Continued learning and professional development in farm animal health management are key aspects of maintaining a proactive and informed approach to animal care.
• Hands-on training experiences, workshops, webinars, and conferences offer valuable learning opportunities for individuals involved in farm animal health management.
• These educational activities provide a platform for farmers to interact with experts, share experiences, and gain insights into new technologies and practices that can enhance the health and welfare of their animals.
• Continued learning and professional development in farm animal health management are key aspects of maintaining a proactive and informed approach to animal care.




